1、 What is chitin?
Chitin, also known as chitin or chitin, is a polysaccharide extracted from the shells of marine crustaceans. Its chemical formula is (C8H13O5N) n.
Mainly derived from animals, it exists in the shells of crustaceans such as shrimp and crabs, the epidermis of insects, and the cell walls of fungi such as mushrooms in nature.

Chitosan has a wide range of applications and can be used in industries such as fabrics, clothing, dyes, paper, and water treatment. Can be used as insecticides and plant antiviral agents in agriculture; Making fish feed in the fishing industry; Cosmetics beauty agents, hair protection, moisturizers, etc; Medical supplies can include contact lenses, artificial skin, sutures, artificial dialysis membranes, and artificial blood vessels.
2、 Derivatives of chitin
Chitosan and chitin are processed by deacetylation to form deacetylated chitin, which is soluble, but the degree of solubility depends on the degree of deacetylation.

Chitosan oligosaccharides, also known as chitooligosaccharides (oligosaccharides) or oligochitooligosaccharides, are obtained by special enzymatic degradation of chitosan. They have a polymerization degree of 2-20 and a molecular weight of ≤ 3000Da. They have many unique functions such as good water solubility, high functional effects, high biological activity, and easy absorption and utilization by organisms. Their effects are 10 times that of chitosan.
Oligo acid, also known as chitooligosaccharides or anionic amino oligosaccharides, is obtained from chitosan through a series of biochemical reactions. Its molecular weight is ≤ 3000Da, it carries a negative charge, has good water solubility, higher biological activity, and is more easily absorbed and utilized by organisms. It retains the acetyl group and its function is several times that of chitooligosaccharides.

Oligomeric iodine is an oligosaccharide product formed by the complexation of oligomeric acid and iodine, which has strong bactericidal function and can effectively kill bacteria, fungi, viruses, and pathogens.
3、 The source of chitin
(1) Arthropods are mainly crustaceans, such as shrimp, crabs, etc., which contain chitin up to 58% to 85%; Next are insects (such as locusts, butterflies, mosquitoes, flies, silkworms, etc.), polypods (such as horsetails, centipedes, etc.), and arachnids (such as spiders, scorpions, ticks, mites, etc., with chitin content of 4% -22%).

(2) Molluscs mainly include the classes Diptera (such as softshell turtles), Gastropoda (such as abalone and snails), Decapoda (such as bivalves), Branchiopoda (such as oysters), and Cephalopoda (such as squid and parrots), with a chitin content of 3% to 26%.
(3) The annelids include three classes: protozoa (such as hornworms), polychaetes (such as sandworms and earthworms), and leeches (such as grasshoppers). Some contain very little chitin, while others can reach as high as 20% to 38%.

(4) Protozoa, also known as protozoa, are single celled animals that include flagellates (such as trypanosomes), carnivorous insects (such as amoebas), sporozoites (such as malaria parasites), ciliates (such as paramecium), etc. They contain less chitin.
(5) Coelacanth animals include Hydra (such as Hydra and Hydra), Jellyfish (such as jellyfish, jellyfish, and coral polyps), etc. They generally contain very little chitin, but some can reach 3% to 30%.
(6) Seaweed is mainly green algae, containing a small amount of chitin.

(7) Fungi include Ascomycota, Basidiomycota, Algae, etc., with chitin content ranging from trace amounts to 45%. Only a few fungi such as Olm ycetes and Triohamycetes do not contain chitin.
(8) Chitin is present in the hard parts of joints, hooves, and feet of other animals, as well as in the joints between animal muscles and bones.
In addition, oligosaccharides such as chitin or chitosan have also been found in plants. In one case, when the plant cell wall is invaded by pathogens, some polysaccharides in the cell wall are degraded into biologically active oligosaccharides, including chitosan. A typical example is the discovery of chitosan at the wound healing site of a tree trunk injury; Another scenario is the lipid oligosaccharides produced by rhizobia, which are also chitooligosaccharides, chitooligosaccharides, and chitooligosaccharides.
4、 Application of chitin in agriculture
Chitin derivatives are made using different processes and can be used to prepare poultry feed, biofertilizers, biopesticides, plant growth regulators, soil amendments, agricultural preservatives, agricultural breathable films, plant fungicides, seed coating agents, insecticides, soil and trace element chelating agents, etc.

1. Increase soil nutrients and improve soil microbial community
Chitin is a good source of carbon and nitrogen, which can quickly supplement organic nutrients in soil and improve the microbial community. After decomposition in soil, it can promote the reproduction of radiation bacteria, naturally antagonize harmful filamentous bacteria, improve soil microbial ecology, and alleviate soil microbial community disorder.

It can accelerate the mineralization and decomposition rate of organic matter (organic fertilizer, straw, etc.) in the soil, decompose into nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, trace elements, and form organic substances such as humic acid and brown humic acid, providing sufficient nutrition for plant growth; Autotrophic nitrogen fixing bacteria can fix nitrogen in the air, increase nitrogen levels in the soil, and reduce the use of nitrogen fertilizer.
2. Stimulate seed germination
Seeds coated with chitin have better germination rates than those without coating. Through a large number of experimental fields, it has been found that in areas with severe fungal invasion, seeds treated with chitin can increase germination rate by about 20%.

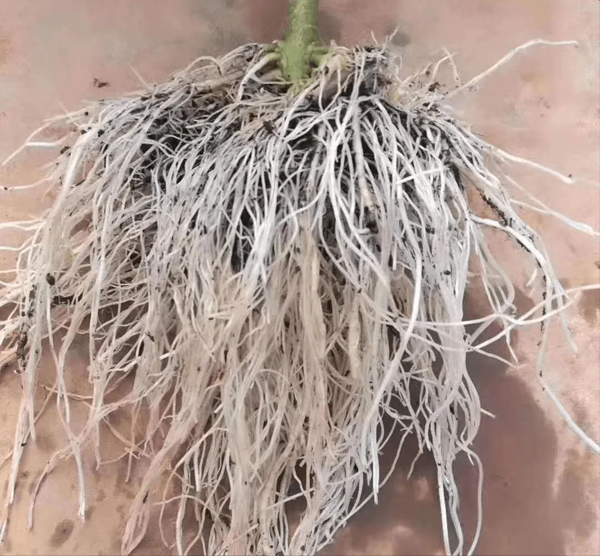
3. Has strong rooting ability and root protection ability
The biggest difference between chitin and ordinary rooting fertilizers is that chitin can promote root rooting, effectively resist damage to roots under ground temperature, and provide normal nutrition to crops even in geothermal environments.
After using chitin in cucumber, a large number of white roots can be seen on the surface of the bed within 3 days, and after 7 days, the plant growth is clearly vigorous.
4. Improving crop immunity and preventing diseases and pests (1) Controlling bacteria
Chitin can stimulate plants to activate their own defense mechanisms, avoiding bacterial harm and promoting crop health.
Chitin can stimulate plants to produce free phenolic compound enzymes and chitin enzymes, which can break down the cell wall of fungi and make them disappear. Plants are not affected by harmful filamentous bacteria, and cells can be activated to promote crop growth and development.
The solution containing chitin, due to its positive charge, will tightly bind with the negative charge on the surface of crop cells, promoting the attachment of fungicides and other small molecule nutrient components to plants to prolong their effects, and stimulating the contraction of leaf pore cells, reducing the chance of fungal invasion.
Chitin easily adsorbs onto the surface of pathogens to inhibit their reproduction, or adsorbs and aggregates with flagella and membranes on the surface of pathogens to prevent their reproduction.
(2) Preventing and controlling insect pests
After spraying chitin on the leaves, the chitin solution acts like wax, fixing the feet or wings of pests until they suffocate and die; In addition, enzymes secreted by chitin can dissolve the hard epidermis of insects and the hard shells of nematode eggs. Make it impossible for pests such as mold, aphids, spiders, etc. to inhabit crops.

5. Natural organic slow-release fertilizer
Chitin can fix nitrogen, hydrolyze phosphorus and potassium, thereby improving the utilization efficiency of fertilizers. Chitin can also stimulate plants' ability to absorb fertilizers, and can be used as a liquid fertilizer for soil improvement; Foliar spraying is an excellent foliar fertilizer, and positively charged polymer can slow down the fertilizer efficiency of other applied fertilizers, increasing crop yields.

The molecular structure of chitin contains amino groups, which can chelate with trace elements such as copper, iron, manganese, zinc, etc., increasing the available nutrients of trace elements in fertilizers. At the same time, it releases the fixed trace element nutrients in the soil for crop absorption and utilization, thereby improving fertilizer efficiency.
6. Improve the quality of crops
We all know that the strength of photosynthesis is the key to crop quality, and the more products of photosynthesis in the fruit, the more comprehensive the nutrition of the fruit. Chitin can alleviate the adverse growth conditions of nine crops and keep them in a suitable growth state, greatly improving their photosynthesis. As photosynthesis increases, the amount of photosynthetic products in the fruit naturally increases, resulting in improved quality.
7. Inducing overall regulation of endogenous hormones
Spraying chitin on plant leaves has the effects of breathability and water retention; Spraying on leaves or applying to soil can promote the division of root cells, promote root development, enhance plant drought and lodging resistance, shorten and thicken stem nodes, make leaves lush and moist, significantly improve photosynthesis, and promote the directional transport of photosynthetic products.
8. Preventing and controlling the occurrence of continuous cropping obstacles

Chitin can produce agglomeration in soil, which can improve the soil cohesion of cohesive soil, thereby promoting soil aeration, water retention, and drainage. It has a good effect on crop root elongation and capillary root development, activating soil and improving the problems caused by continuous cropping.
5、 Selection of chitin fertilizer
Because chitosan fertilizer is a new type of fertilizer, it has increased the difficulty for farmers to choose. So how to choose chitosan fertilizer?
At first glance at the implementation standards: In 2002, the Ministry of Agriculture approved chitosan fertilizer as an organic soluble fertilizer, so qualified chitosan fertilizers must have a fertilizer registration certificate number and implementation standards;

Secondly, let's take a look at brand services: As chitosan is a new type of fertilizer, for some small businesses, it is difficult to achieve qualified production capabilities and ensure product quality. Therefore, in terms of selection, it is particularly important to distinguish it from traditional fertilizers and choose products produced by large companies in order to provide service and after-sales guarantee;
Check the content three times: Chitosan fertilizer is labeled on the packaging with the content of chitosan or chitin, so the level of content directly affects the quality of the product;

Four factors to consider: Chitosan fertilizer belongs to slow-release fertilizers, which is also the reason why the promotion progress is slow.
There is a saying circulating in the fertilizer industry about the effect of chitin: "It works once, it works twice, and it works wonders three times." This means that after using it once, crops can absorb chitin, but it is difficult to judge with the naked eye; After using it twice, the effect becomes apparent, including an increase in root system, color of leaves, and growth of plants, all of which are significantly different from those that were not used;
After using it three times, both the growth and development of crops and the yield and quality of fruits will receive magical effects.
6、 Application method of chitin
In terms of use, the most common methods of chitosan fertilizer are currently through flushing and spraying:
Chongshi: Applying 600-800 times chitosan solution to the roots of crops can promote rooting and seedling strengthening, promote the growth and development of crop roots, enhance root vitality and rooting ability.

Spraying: Spraying with a 300-500 fold solution before flowering and during the fruiting period of crops can promote plant growth and greatly improve crop fruiting and fruiting.
Spraying three times in a row with an interval of 7-10 days will yield unexpected results. Of course, many companies also add chitin as an additive to agricultural products to increase their added value.